Published on 2024-04-12

Micro injection molding is gaining popularity in mass production for its ability to efficiently and accurately manufacture small-scale products. This method stands out from traditional manufacturing processes, which often struggle to achieve high precision with miniature items.
To deepen your understanding of this essential manufacturing technique, we provide introductory insights into micro injection molding, highlighting its benefits for producing small-scale products.
Table of Contents
What is Micro Injection Molding?
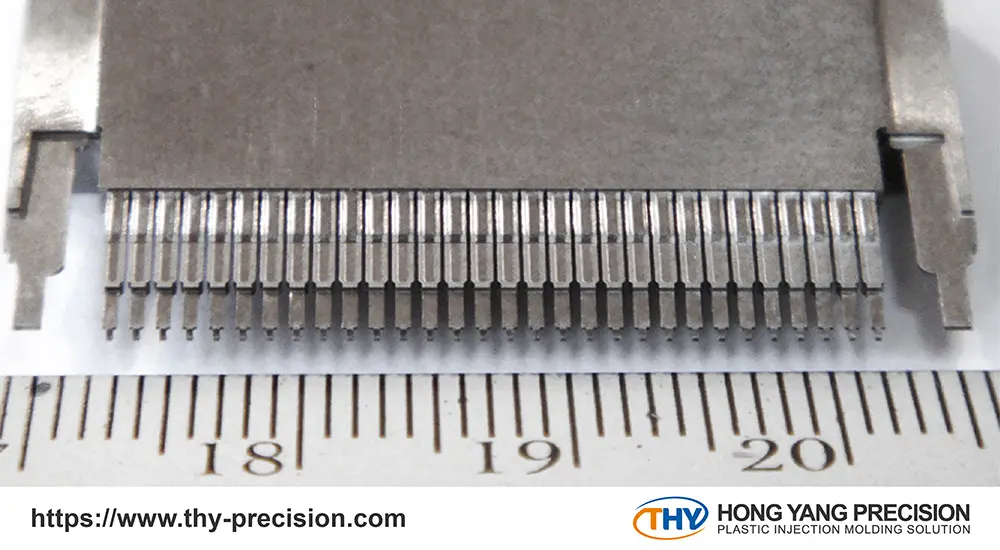

Micro injection molding is a pivotal manufacturing technique in today’s industry, celebrated for its high precision with tolerances ranging from 10 to 100 microns and the ability to produce components weighing less than 1 gram.
Micro injection molding offers cost-effective solutions for the high-volume production of precise products, including medical components, optical parts, and electronic devices.
The Key Considerations in Micro Injection Molding
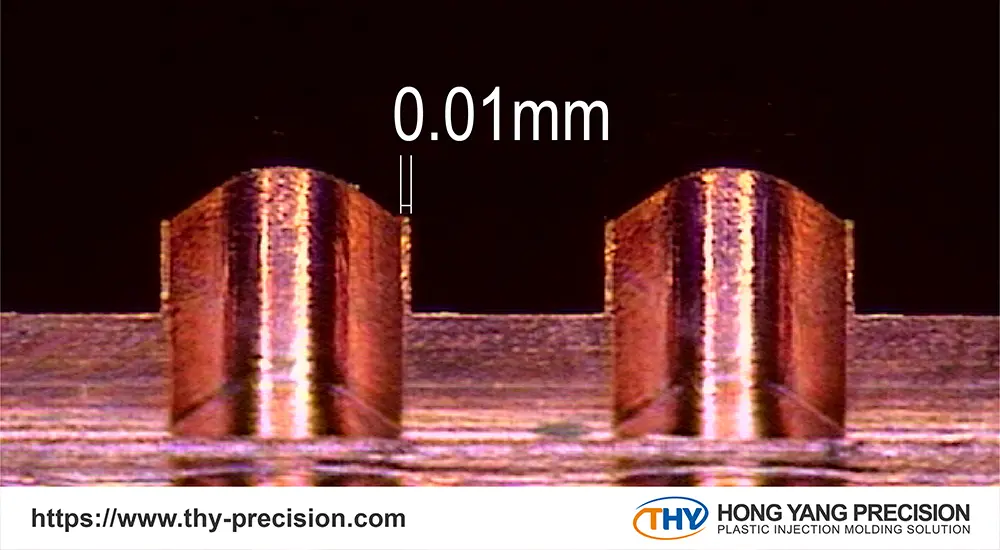
Micro-molding machines, boasting high-resolution feed options, are capable of injecting minuscule fractions of a gram with remarkable precision. This precision facilitates uniform pressure distribution within the mold cavity.
In comparison to conventional injection molding techniques, micro injection molding shines in its ability to consistently produce parts with tight tolerances during mass production.
Not only does it excel in producing high-quality components, but micro injection molding is also the preferred method for manufacturing parts that require the use of high-performance polymers, such as Liquid Crystal Polymers (LCP).
Apart from these characteristics of micro injection molding, there are several crucial factors might affect the outcome of the products:
Mold Complexity
Achieving tight tolerances in products is often seen as a challenging aspect of the process, but the role of a highly accurate and precise mold, especially at the micro-scale, is critical to product precision. Crafting a mold that captures intricate details can be expensive, yet it’s a worthwhile investment.
Repeatability
Ensuring uniform product size in mass production presents a challenge, which becomes even more complex at the micro-scale. Addressing this issue demands the precision tolerance of tooling and meticulous control throughout the entire micro injection molding process.
Material flow and cooling control
Ensuring consistent material flow and maintaining a uniform temperature throughout the cooling process in micro injection molding presents its own set of challenges. Achieving the desired material flow requires careful management of injection speed, pressure, temperature, moldflow analysis, and mold gate design to ensure that the material flows correctly.
You can read more about design guidelines for precision injection molding in this article.
Difference Between Micro and Conventional Injection Molding
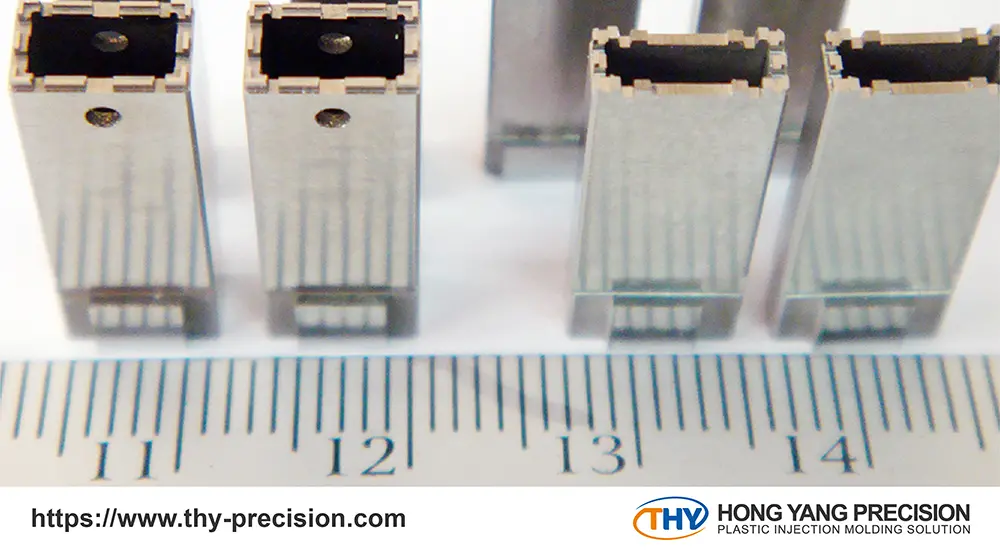

Micro injection molding is a highly efficient method for mass-producing small-scale products, yet it differs from traditional injection molding in several key aspects.
To determine the most suitable production technique for your products, it’s important to consider these differences carefully.
Shot Sizes
Unlike traditional injection molding, micro injection molding facilitates the production of parts with a minimum weight of just 1 gram. This capability leads to less material waste for users when manufacturing the same parts through micro injection molding.
Precision and Complexity
This advanced injection molding technique is renowned for its outstanding precision and ability to manufacture complex components. In contrast to conventional injection molding, micro injection molding specializes in producing parts with micro-level tolerances.
This is crucial for industries such as medical devices, electronics, and optics, where even slight variations in size or subtle differences in surface texture can significantly impact performance.It ensures the precise replication of complex designs, resulting in accurate and reliable parts.
Material Selection and Compatibility
The adaptability to use various materials enables the creation of parts specifically designed for distinct applications. By carefully choosing materials, it’s possible to enhance biocompatibility, electrical conductivity, and thermal resistance, among other properties. This flexibility in selecting materials guarantees that the micro molded components fulfill the exact functional specifications required.
Application of Micro Injection Molding

Micro injection molding is particularly well-suited for the production of medical, optical, and electronic components. For medical parts, we utilize a clean room certified under ISO 13485, enabling clients to produce high-quality, clear products for hospital use or clinical trials without the risk of contamination.
In the realm of optical parts, this process excels at creating non-flat substrates on a micro scale—a task that presents significant manufacturing challenges. Moreover, it facilitates the production of optical fibers used for high-speed data transmission, delivering high quality at low cost due to the efficiencies of micro injection molding.
Micro injection molding offers a cost-effective and efficient method for producing electronic components, including connectors for high-speed signals, on a small scale. The compact size of these components is essential for the advancement of electronic devices, enabling them to support high-speed signal functionalities more effectively.
Conclusion
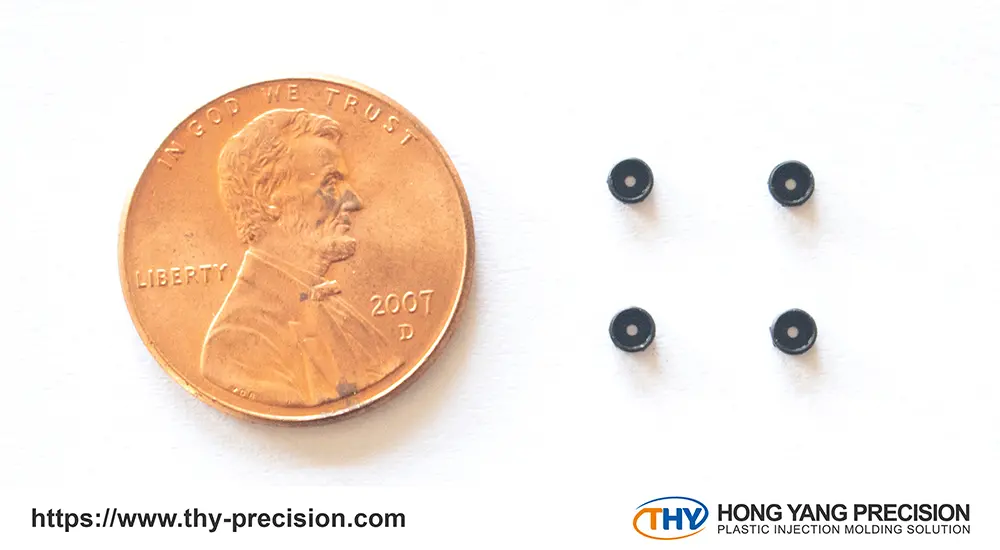

For further details on how micro injection molding can benefit your specific field, please feel free to reach out to us. Our experienced team of micro injection molding specialists is ready to offer you the optimal solutions for your products.




Learn more about injection molding:
In-Depth Look at Injection Molding Machine Types & Uses




